Abstract
Introduction: MPNs are chronic malignancies associated with significant morbidity and mortality due to cardiovascular events (CVE) and progression to more aggressive myeloid neoplasms (progression). CVE, progression, and survival are not feasible clinical trial endpoints due to the long follow-up required for analysis, leading to use of short-term measures. A reliable biomarker linking MPN biology with these important outcomes would facilitate development of new agents that can meaningfully reduce these risks and improve survival. Ultimately, MPNs result from hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) acquisition of highly recurrent driver mutations, most commonly JAK2 V617F. Here, we study MPN fitness - the competitive advantage of mutated hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPC) over their normal counterparts- as a prognostic and monitoring biomarker in MPNs, and compare it to whole blood (WB) mutation allele frequency (MAF).
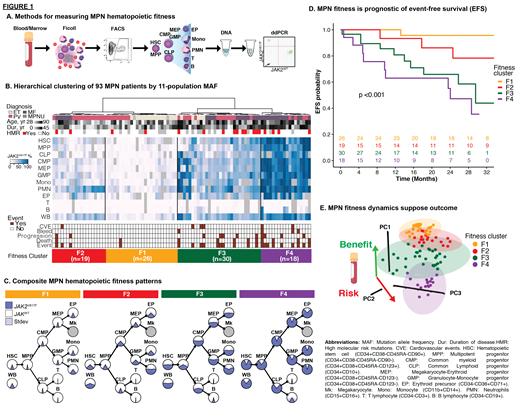
Methods: We measured fitness by sorting peripheral blood (PB) specimens from MPN patients (pts) at Weill Cornell Medicine (WCM) into 11 well-defined and strictly validated immunophenotypic HSPC and mature cell compartments and measured MAF in each and in WB (Fig 1A). The study was approved by WCM institutional review board. Pt age, sex, diagnosis (Dx), duration of disease (Dur), symptoms, blood counts, mutations, spleen size, treatment, follow-up, and events (CVE, progression, death) were tabulated. Principal component (PC) analysis was used for unsupervised hierarchical clustering of 11-population MAFs to identify predominant patterns of fitness. Event-free survival (EFS) was assessed using Kaplan-Meier (KM) methods and log-rank test. Cox multivariable analysis (MVA) of EFS was used to assess the independent prognostic value of baseline MPN fitness, compared to WB MAF. A Cox model was used to translate change in fitness (PCs 1-3, Fig 1E) from serial samples into a relative risk of events. A Fisher's test was used to determine if changes in fitness were associated with events and/or IWG-MRT/ELN response (Barosi et al. & Tefferi et al. Blood 2013).
Results: A total of 212 PB samples from 93 JAK2 V617F MPN pts with essential thrombocythemia (ET, n = 20, 22%), polycythemia vera (PV, n = 39, 42%), myelofibrosis (MF, n = 32, 34%) or unclassified MPN (MPNU, n = 2, 2%) were prospectively collected between 7/2017-7/2021 and analyzed. Median age was 68 years (yr) (range 28-90) and median Dur was 6 yr (0-45). The majority were females (n=58, 62%). Unsupervised PC clustering at baseline revealed 4 major fitness levels (FLs): F1, F2, F3, and F4 (Fig 1B). The pattern of JAK2 V617F propagation from HSPC to mature lineages differed across FLs (Fig 1C). EFS was strongly (KM, p<0.001, Fig 1D) and independently (Cox MVA) associated with FL when covariates of age, sex, Dx, Dur, and WB MAF were considered (F2, 3, 4, versus F1: HR of 7 [p=0.15], 31 [p=0.009], and 92 [p=0.009], respectively). In contrast, EFS was not statistically linked to WB MAF quartiles in KM analysis (p=0.06) and was not associated with WB MAF in MVA (HR 0.97, p=0.06). We developed a Cox model to predict relative risk of events from serial fitness measures and tested the model in 25 pts. Pts with increased fitness were more likely to experience an adverse event (33% vs 0%, p=0.047) and were less likely to achieve clinical response (13% versus 75%, p=0.007) than pts with decreased fitness. Change in WB MAF did not correlate with change in fitness (r 2=0.0116) and did not predict events (p=1) nor clinical response (p=0.23).
Discussion: Reliable biomarkers are needed to efficiently identify disease-modifying treatments mitigating the risk of progression and other adverse events. Our study offers a feasible approach to monitor risk by tracking MPN fitness in clinically accessible PB specimens. In this large study, MPN fitness outperformed WB MAF as a biomarker and was highly prognostic of EFS. Fitness dynamics were strongly predictive of events and clinical response whereas changes in WB MAF were unreliable. Methods to simplify routine measurement of MPN fitness are being developed to support clinical trials. Updated validation of MPN fitness as a biomarker in clinical trials will be presented.
Conclusion: MPN fitness may serve as both a prognostic biomarker identifying MPN pts at high risk of disease-related events and a monitoring biomarker for use as a short-term surrogate of long-term outcomes in clinical trials.
Abu-Zeinah: PharmaEssentia: Consultancy. Ritchie: ARIAD Pharmaceuticals: Ended employment in the past 24 months, Speakers Bureau; Protaganist: Consultancy, Honoraria; Bristol Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Research Funding; NS Pharma: Research Funding; Astellas: Consultancy, Research Funding; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: travel support, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Incyte: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Celgene/BMS: Consultancy, Other: travel support, Speakers Bureau; Abbvie: Consultancy, Honoraria; Jazz: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding. Silver: Abbvie: Consultancy; PharamEssentia: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau. Scandura: MPN-RF (Foundation): Research Funding; Abbvie: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Constellation: Research Funding; CR&T (Foudation): Research Funding; European Leukemia net: Honoraria, Other: travel fees .

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal